Single cell microfluidic chip |
We developed microfluidic chips that use very minute amount (pL ~ nL) of fluid to do and control cell assays even up to the single cell level. In particular, we measured the enzyme activity of individual cells in micro-compartments generated by controlled flow of oil and aqueous double phases. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol., 109, 285-350, 2008, Review.
|
|
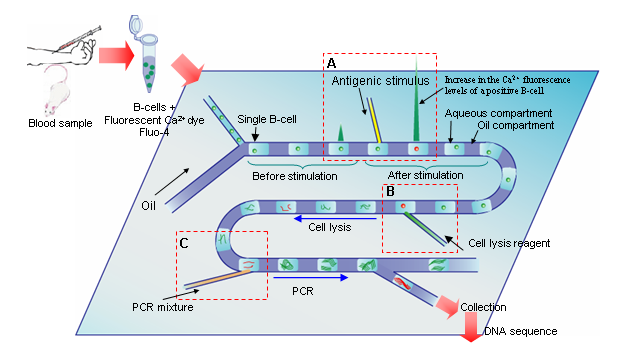
Figure 1 Schematic illustration of novel compartmental microfluidic chip devices for micro total analysis system, which encompasses (a) single-cell sorting, screening, analysis of active cell against a stimulant, (B) single cell lysis, (C) PCR and retrieval of antibody DNA of positive cell from a specific compartment.
|
|
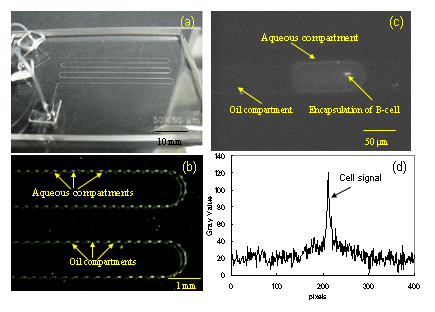
Figure 2. Photograph of a microfluidic device (a), bright filed micrograph showing picoliter level aqueous and oil compartments in the microchannel (b), fluorescent microscopic image showing the entrapment of single B-cell in the aqueous compartment and corresponding cell signal (d).
|
|
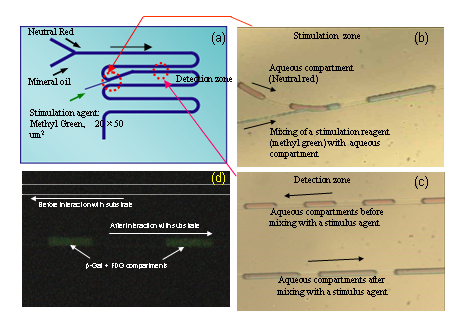
Figure 3. Illustration showing the chip device for on-chip single-cell stimulation (a), stimulation zone showing the mixing of stimulation reagent with aqueous compartments (b), detection zone representing aqueous compartments before and after stimulation reagent mixing (c), on-chip β-galactosidase assay, showing generation of fluorescence in the microchannel after FDG substrate mixing with β-galactosidase compartments (d).
|
|
|
|
|
大阪大学 大学院工学研究科 精密科学・応用物理学専攻 応用物理学教室 民谷・朝日研究グループ
Department of Applied Physics, Osaka University, Suita, Osaka 565-0871
|
|

